Three scientific directions:
Three distinct but interrelated research directions are active in the laboratory:
Cellular systems in muscle regeneration
We use acute and chronic damage in adult mice to elicit regeneration in muscle. Using this model, we have identified important roles for mesenchymal progenitors and monocyte/macrophages in ensuring proper regeneration. Our goal is to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying such roles.
Cellular systems in muscle regeneration
We use acute and chronic damage in adult mice to elicit regeneration in muscle. Using this model, we have identified important roles for mesenchymal progenitors and monocyte/macrophages in ensuring proper regeneration. Our goal is to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying such roles.
|
|
|
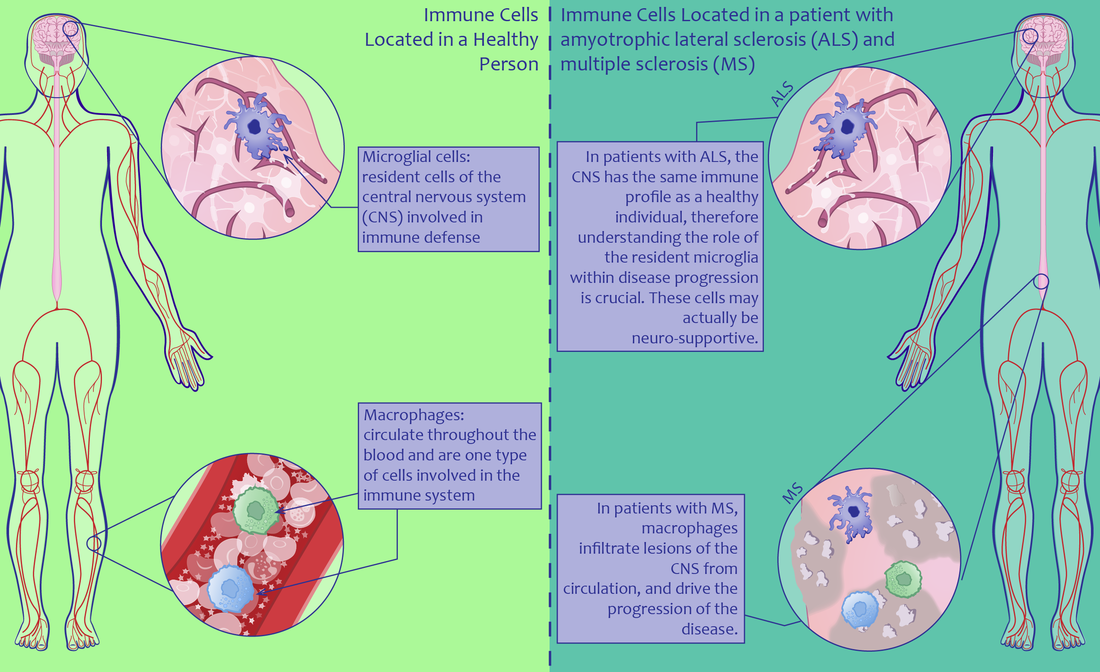
Microglia/macrophages in CNS pathology
We use parabiosis (the surgical joining of two immunocompatible animals leading to complete blood exchange) in combination with transgenic tools to study the relative role of local and blood-derived myelomonocytic cells to CNS pathologies.
We use parabiosis (the surgical joining of two immunocompatible animals leading to complete blood exchange) in combination with transgenic tools to study the relative role of local and blood-derived myelomonocytic cells to CNS pathologies.
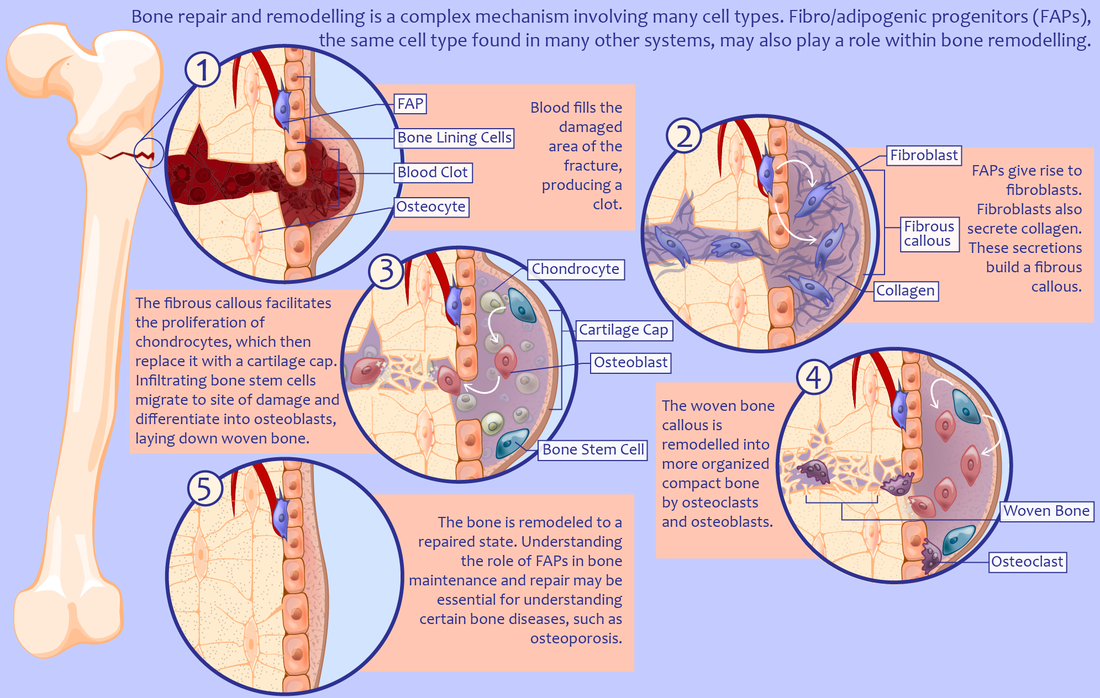
FAP contribution within bone remodelling after damage
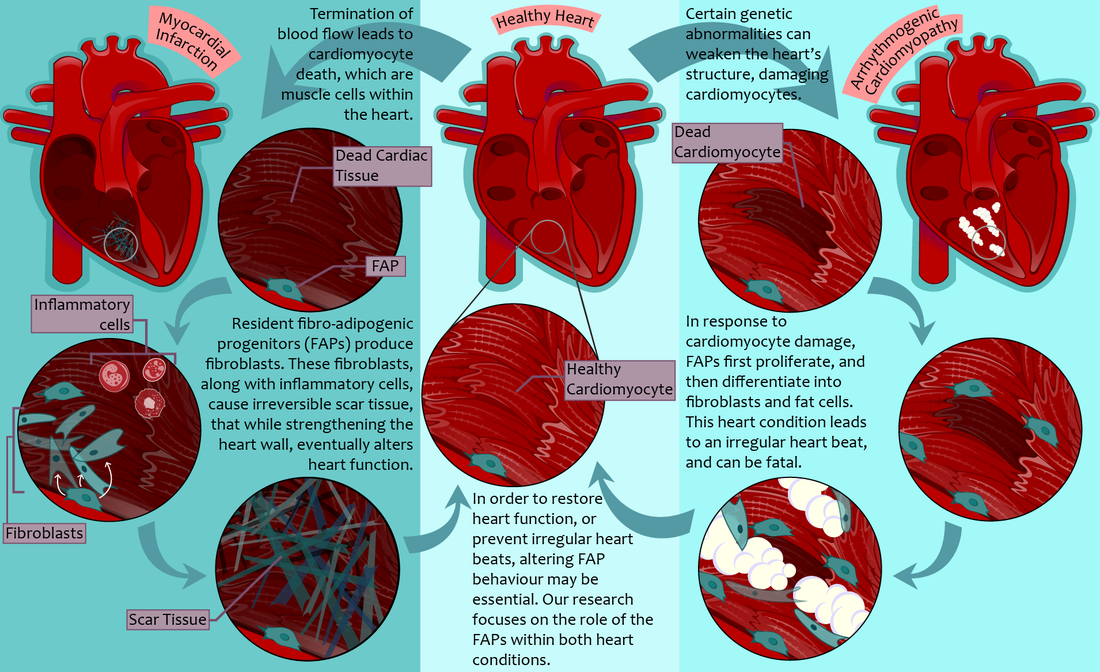
Investigation of cardiac-resident FAPs within the heart pathologies, myocardial infarction and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
Epigenetic control of lineage choice/differentiation
We generated floxed alleles of two methyltransferases, SET7/9 and G9a/EHMT2, to study their role in regeneration. Using these tools we have uncovered unexpected roles for these enzymes in hematopoietic and myogenic cells that are currently under active investigation.
We generated floxed alleles of two methyltransferases, SET7/9 and G9a/EHMT2, to study their role in regeneration. Using these tools we have uncovered unexpected roles for these enzymes in hematopoietic and myogenic cells that are currently under active investigation.